United Nations (UN) adopted a resolution in 2017 declaring 2018-28 as the international decade for action on water for sustainable development. Water is an important resource for the development of any society and helps maintain the integrity of the ecosystems. Water management is very essential to get food security and prevent soil erosion. About 60% area in India is still rain-fed so monsoon rains play a significant role in India.
Average rainfall in India is 1183 mm out of which 75% is received during the monsoon period i.e. July to September. This results in runoffs during the monsoon period and thus there is a need to work on rainwater harvesting to save water for the rest of the year. Even if 5% of water is harvested, it would produce a substantial quantity of water to the tune of 900 million litres.
Mostly the rainwater harvesting system involves three components the catchment area, the collection device and the conveyance system. Two methods are usually adopted for harvesting rainwater: i) Surface rainwater collection and ii) Rainwater from roofs.
The surface rainwater could be caught and used for recharging aquifers. In rooftop harvesting, the roof becomes the catchment and is collected from the roof of buildings and stored in tanks or diverted to an artificial ground recharge system. It is less expensive than the former method for recharging the groundwater as,
1) Pits are constructed for recharging the shallow aquifers. Constructed with a width of one to two metres and a depth of around three metres backfilled with boulders or coarse sand.
2) Trenches: These are constructed when the permeable straits are available. The trench may be 0.5 to 1 m wide, 1 to 1.5 m deep and 10 to 15 m long. They are backfilled with filter material.
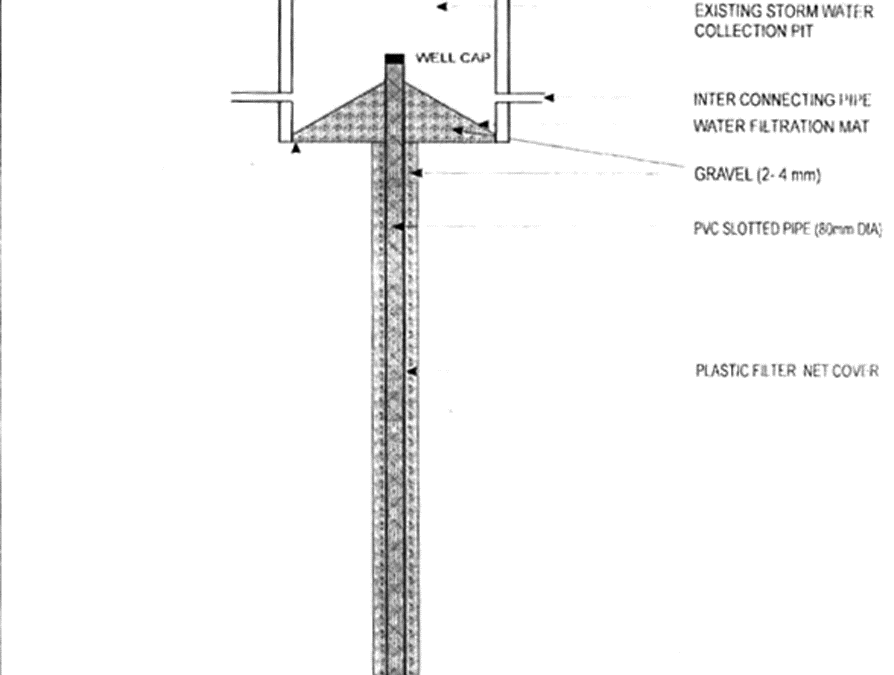
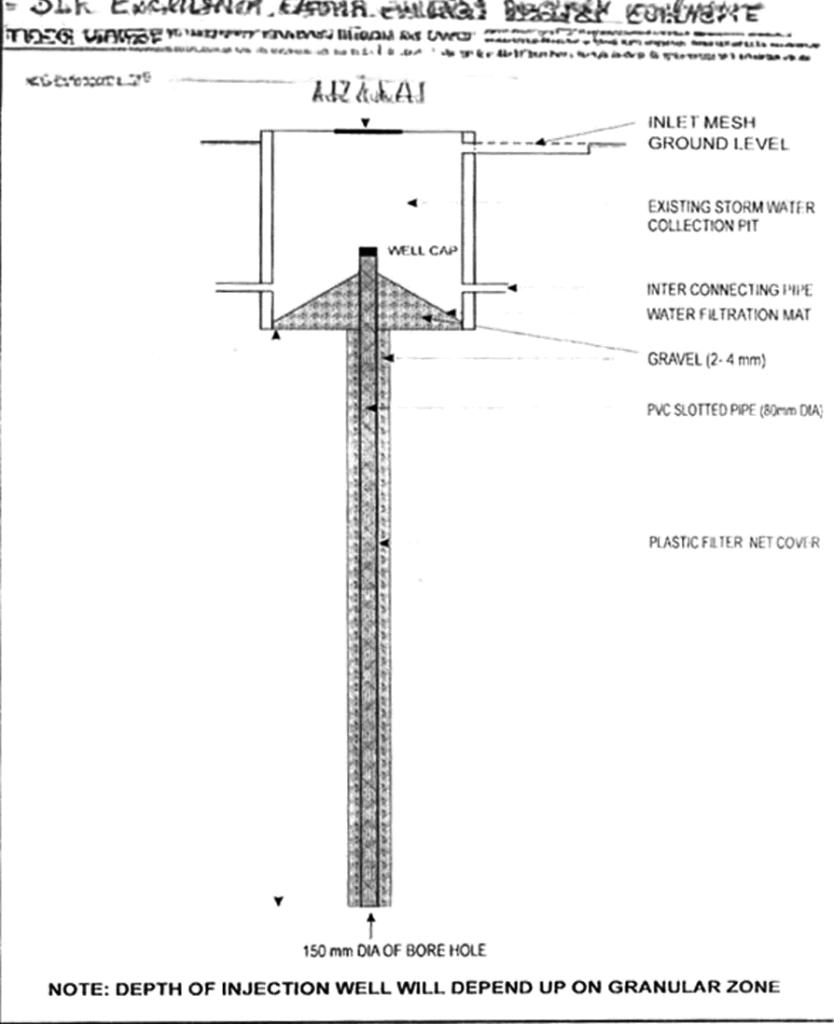
3) Recharge shafts: Recharging of the aquifer below the clayey surface, shafts of 0.5 to 3 m diameter and perforated pipes 10 m to 15 m deep are constructed and backfilled with gravel and coarse sand.
4) Rooftop rainwater: The rainfall that has accumulated on the building roof is directed to a storage tank. Before connecting to a storage tank, each drain pipe or gutter should have a filtering system and a mesh filter at the mouth of the gutters. Provision for excess water flow should be present in the tank. Water from storage tanks may be utilised for gardening and washing. To prevent contamination in storage from atmospheric and rooftop pollutants, a mechanism called first flush is used to remove water from the first shower.
The system adopted in exclusive floors by DLF is that surface runoff is diverted to shafts through concrete pipes with varying depths between six ft. to nine feet. At the bottom, a fine wire mesh is placed acting as a filter so that clean water free from mud and dried leaves flows down through six inches of perforated pipe beneath the ground by fifteen to twenty meters. We have around twelve harvesting pit stands constructed in the D06 and D09 lanes by DLF.
The union government also supplements the efforts of states on water conservation and its harvesting through technical and financial support. One of the major initiatives of the government ‘The Jal Shakti Abhiyan’, “Catch the Rain”, 2022 mission was launched in March 2022 in all districts of India for water conservation and rainwater harvesting. While the National Water Policy advocates water conservation and rainwater harvesting, the Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) also focuses on rainwater harvesting.
Hope in the coming years water harvesting proves to be a boon for humanity.
Popular Stories
How To Revive Your Rainwater Harvesting System
The Water Couple’s Journey: From Cleaning Tanks to Complete Water Solutions!
Locals Felling Trees Near Sec A Pkt C
Winning Has Become a Habit for Divya
Is Green Park Heading Towards A Slum
Haphazard Parking, Narrow Walking Space In M Block Market
Recent Stories from Nearby
- Women’s Day-Vasant Kunj Ambassador In Noida! March 26, 2025
- Free Multi-Specialty Health Camp in D-3/4! March 26, 2025
- Pride of Vasant Kunj! March 26, 2025
- Self-Defense Classes March 26, 2025
- Rang Barse: A Vibrant Extravaganza March 26, 2025